San Salvador Times
The Pulse of El Salvador’s Transformation
Saturday, Jan 10, 2026
San Salvador Times
OpenAI's o3 AI Model Reaches Human-Level Capability on General Intelligence Evaluation
OpenAI's o3 AI model attains a significant achievement, attaining human-level performance on the ARC-AGI benchmark, igniting discussions about the possibilities of artificial general intelligence.
In a major advancement, OpenAI's o3 system has reached human-level performance on a test intended to assess general intelligence.
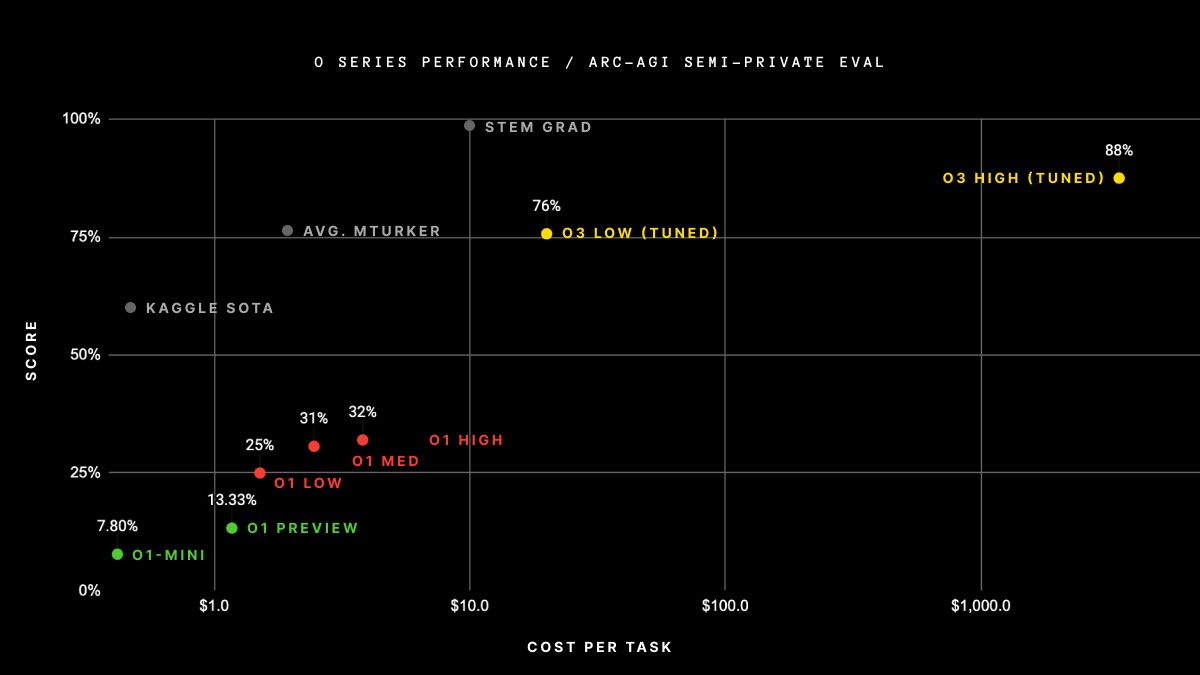
On December 20, 2024, o3 attained an 85% score on the ARC-AGI benchmark, surpassing the previous AI record of 55% and equaling the average human score.
This signifies a pivotal moment in the quest for artificial general intelligence (AGI), as the o3 system excels in tasks that evaluate an AI's ability to adapt to new situations with limited data, which is a crucial indicator of intelligence.
The ARC-AGI benchmark evaluates AI’s 'sample efficiency'—the ability to learn from few examples—and is considered a crucial step towards AGI.
Unlike systems like GPT-4, which depend on large datasets, o3 demonstrates proficiency in situations with minimal training data, a significant challenge in AI development.
Although OpenAI has not fully revealed the technical specifics, o3’s success might be due to its capability to identify 'weak rules' or simpler patterns that can be extended to solve new problems.
The model likely explores several 'chains of thought,' choosing the most effective strategy based on heuristics or fundamental rules.
This approach is similar to methods used by systems like Google’s AlphaGo, which employs heuristic decision-making to play the game of Go.
Despite these encouraging results, questions remain about whether o3 truly represents progress toward AGI.
There is speculation that the system might still be leveraging language-based learning rather than genuinely generalized cognitive abilities.
As OpenAI shares more details, the AI community will require further testing to evaluate o3’s true adaptability and whether it can match the breadth of human intelligence.
The ramifications of o3’s performance are substantial, particularly if it proves to be as adaptable as humans.
It could herald a new era of advanced AI systems capable of addressing a vast range of complex tasks.
However, fully comprehending its capabilities will necessitate additional evaluations, leading to new benchmarks and considerations for the governance of AGI.
On December 20, 2024, o3 attained an 85% score on the ARC-AGI benchmark, surpassing the previous AI record of 55% and equaling the average human score.
This signifies a pivotal moment in the quest for artificial general intelligence (AGI), as the o3 system excels in tasks that evaluate an AI's ability to adapt to new situations with limited data, which is a crucial indicator of intelligence.
The ARC-AGI benchmark evaluates AI’s 'sample efficiency'—the ability to learn from few examples—and is considered a crucial step towards AGI.
Unlike systems like GPT-4, which depend on large datasets, o3 demonstrates proficiency in situations with minimal training data, a significant challenge in AI development.
Although OpenAI has not fully revealed the technical specifics, o3’s success might be due to its capability to identify 'weak rules' or simpler patterns that can be extended to solve new problems.
The model likely explores several 'chains of thought,' choosing the most effective strategy based on heuristics or fundamental rules.
This approach is similar to methods used by systems like Google’s AlphaGo, which employs heuristic decision-making to play the game of Go.
Despite these encouraging results, questions remain about whether o3 truly represents progress toward AGI.
There is speculation that the system might still be leveraging language-based learning rather than genuinely generalized cognitive abilities.
As OpenAI shares more details, the AI community will require further testing to evaluate o3’s true adaptability and whether it can match the breadth of human intelligence.
The ramifications of o3’s performance are substantial, particularly if it proves to be as adaptable as humans.
It could herald a new era of advanced AI systems capable of addressing a vast range of complex tasks.
However, fully comprehending its capabilities will necessitate additional evaluations, leading to new benchmarks and considerations for the governance of AGI.